Request a qoute.

Sulfide emissions - a global problem with local consequences
Sulfur is life-sustaining element, present in all living entities and is a key ingredient in all cells. Hence, all chemical and biological process in operation today, both in industrial plants and public utility facilities, face sulfur based by-products challenges daily. By far, the most common are hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and their organic equivalents mercaptans (R-SH) or disulfide compounds (RS-SR). Mellifiq offers complete solutions to these problems which, if not managed properly, may present severe hazards.
Types of sulfur-based emissions and compounds
Elements of sulfur is an omni-present problem. Since it is present in all living cells, sulfur emissions are generated as by-product in many processing facilities and waste management plants, in most cases where oxygen-deprived conditions govern the process. These conditions promote anaerobic conditions in which microorganisms produce reduced forms of sulfur, normally in the form of H2S, mercaptans or disulfide compounds.
Hydrogen sulfide, H2S, is free non-organic form of sulfur formed where large amounts of substrates are available along with bacteria capable of metabolizing the substrates anaerobically and which generate concentrations up to 3,000 ppm in some industrial processes.
Hydrogen sulfide is known for its pungent odor, corrosive characteristics and toxicity for human beings. It is therefore imperative to treat or prevent formed H2S levels to acceptable limits in terms of EHS and environmental regulations.
Mercaptans are organic forms of sulfur compounds which may be formed under anaerobic conditions, just like H2S, but also exist naturally. They are described chemically as R-SH where “R” marks a generic organic chain and “-SH” is the functional group sulfhydryl. Just like H2S, the are also the source of pungent odors even in ppb or low ppm levels. Disulfide compounds occur in nature as an organic sulfide form but without a sulfhydryl functional group.
It must be noted that most point sources of sulfide compounds generate emissions composed of a variety of the abovementioned types, which differ over time depending on available substrates and conditions.
Biogas – anaerobic digestion
One of the most prominent industrial settings where high concentrations of hydrogen sulfides are generated is biogas production from anaerobic digestion, where biogas is generated from from either dry waste or from sludge produced in wastewater treatment plants. In these applications, H2S is a by-product which is formed in high concentrations which must be lowered in order to prevent corrosion or to comply with legal standards for using biogas as fuel in methane upgrading. Mellifiq frequently provides solutions for the biogas industry. Hydrogen sulfide levels may exceed 3,000 ppm following anaerobic digestion in biogas production.
Pump stations
In pump stations, municipal wastewater provides a constant feed of sulfur-rich substrates naturally occuring in raw sludge. In many cases, wastewater is subject to long residence times with non-mixed conditions which generate oxygen-deprived conditions which causes sulfides to form. Often, H2s and mercaptan levels can exceed 200-300 ppm, which is enough to pose serious health hazards and toxicity upon human exposure. Over time, it will also cause a corrosive environment which may degrade concrete foundations and impact exhaust piping and fans.
Other industries
Low concentrations of sulfides are also seen in yeast or food processing plants, where sulfur-containing organics are released along with other VOCs. Pulp and paper processing is another industry where large amounts of mercaptants can be formed from lignin processing. Anarobic conditions are also common in the off-shore industry where Sulfate Reducing Bacteria (SBR) is naturally occurring, producing pipeline corrosion from hydrogen sulfide formation.

Corrosion of pipeline is a severe operational problem and is many times caused by conditions under which hydrogen sulfides and other sulfide compounds are formed.

Hydrogen sulfide is generated as a by-product in high concentrations is anaerobic digestion biogas plants.
| Sulfide | Chemical structure | Description and sources |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen sulfide | H2S | Formed at high concentration in anaerobic digestion process, pump stations, primary treatment of wastewater treatment plant. Reduced free form of sulfide. |
| Mercaptants | R-SH | Versatile list of sources including process industries, food production and pump stations. It is a VOC with bound sulfur and the “R” groups represent various forms of hydrocarbon chains. |
| Disulfides | RS-RS | Alternative form of mercaptans with two sulfur bounds to hydrocarbon chains. May form in conjunction with hydrogen sulfides and mercaptans in pump stations or other anaerobic environements. |
Different types of sulfides formed under anaerobic conditions. All forms may be encountered in low and high concentration up to hundreds or thousands of parts per million in applicable air exhausts.
Mellifiq solutions for sulfide emissions
Mellifiq specializes in sulfide removal and can display an extensive resume of projects and engineering in the field. The key to successful and effective sulfide removal is to implement the correct technology for each case, which depends on multiple factors such as concentration, type of sulfides, air flows and customer-specific requests such as reduction levels and available modes of installation.
The quintessential method for removal is to transform sulfides into non-harmful constituents, which is viable via either a combination of systems from Mellifiq’s Nodora and Ozonetech proprietary brands. In addition, Mellifiq can tailor bespoke solutions to accommodate for limit available installation footprint and even elimination of the sulfides levels and their generated odors. It is possible to employ our engineering services such pilot projects to evaluate and design a specific solution.

Ozonation provides effective H2S removal at low operational cost
One of the most effective and versatile methods to combat both high and low concentrations of H2S, mercaptans and disulfides is through ozonation oxidation. While sulfides presents a challenge for most operations, these substances are prone to degradation if exposed to potent oxidation methods which are easy to retrofit into existing processes. Ozonation degrades and neutralizes sensitive R-SH groups or H-S bonds via oxidation, converting it to sulfur oxides and water. The reaction is straight-forward with zero order kinetics. Ozonetech RENA Pro turn-key ozone systems have been developed with effective sulfide removal in mind for quick and easy installation in existing exhaust ducting.
Nodora CAT for regenerative catalytic treatment
The overwhelming demand for sulfide removal has sparked the development for highly effective, stand-alone units using catalytic inorganic granules for very high levels of hydrogen sulfide applications.
Especially suitable for biogas and methane upgrade implementations, our Nodora CAT line is also suitable for situations where elimination of sulfides are important. The CAT A- and B-series are designed for up to 10,000 m3/hr per unit, exceeding most needs where high hydrogen sulfide levels are at play. The active sulfide-reducing media in our CAT product line is continuously regenerated and can be boosted in combination of upstream ozonation.
Adsorption for organic sulfides including mercaptans
While oxidation and catalytic methods are widely applied by Mellifiq, situations where industrial exhaust air is composed of both non-sulfur based VOCs and sulfides, complementary adsorption may provide sufficient effect. The overall approach is summarized in the table below.
In lieu of targeting the active sulfide groups of H2S, mercaptans and disulfide compounds, non-polar sites of short or long hydrocarbon chains be can utilized to achieve physical adsorption. At Mellifiq, we supply these solutions from our Nodora ADS product line.
| Technology | Recommended system | Operating principles |
|---|---|---|
| Ozonation | Ozonetech RENA Pro turn-key ozone systems | Oxidation of chemical bonds in R-SH, R-S, H-S-H groups |
| Regenerative catalytic reactions | Nodora CAT | Chemically induced catalytic reaction with inorganic granules in closed reaction chambers |
| Adsorption | Nodora ADS with modified media | Adsorption of non-polar hydrocarbon sites of mercaptans and organic disulfides |
Overview of Mellifiq special solutions for reduction or complete elimination of organic or inorganic sulfides.
Combined technology in tailored design satisfied even the most harsh demands
There are situations where applying a single-technology approach may not cut it. Such conditions may involve:
- High air flows
- High concentrations of sulfides
- Significant amount of non-sulfide VOCs
- Near-zero emission requirements or variable concentrations
- Expectation on low operating cost and a self-sustaining operation with minimal interference or maintenance
At Mellifiq, we embrace such challenges. We offer design and engineering expertise to analyze and tailor a complete solution, often incorporating all our cumulative experience and systems offering from across our portfolio of brands. An engineered solution may involve applying a combination of oxidation, adsorption and catalytic treatment to achieve all the above-listed requirements above, or more.

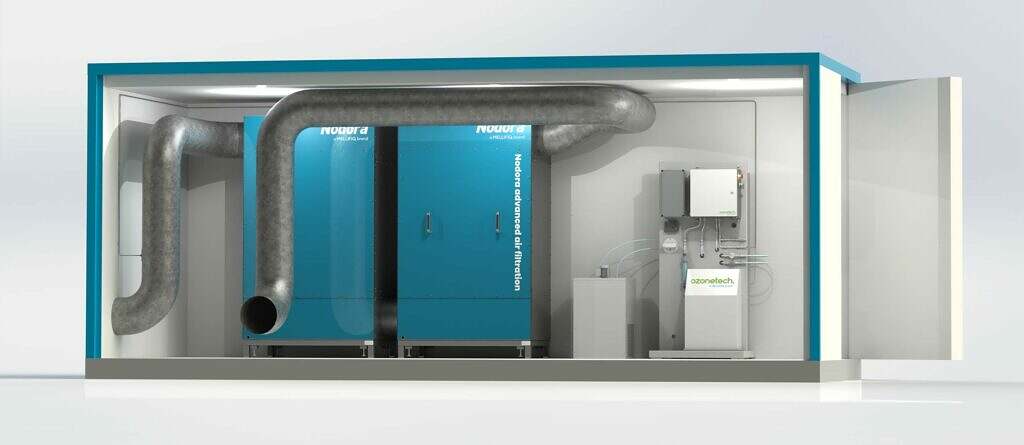
Related reference project.







